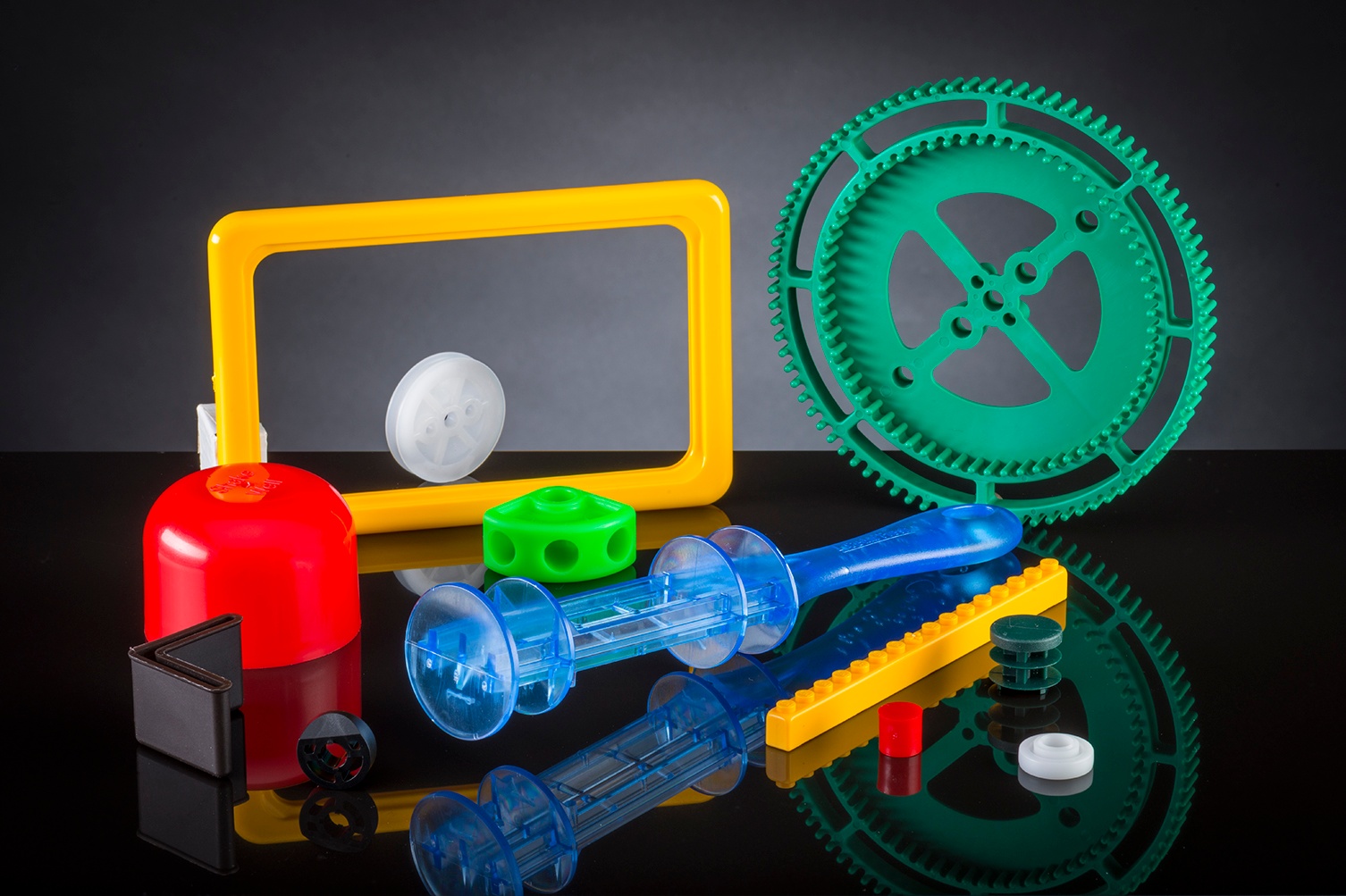
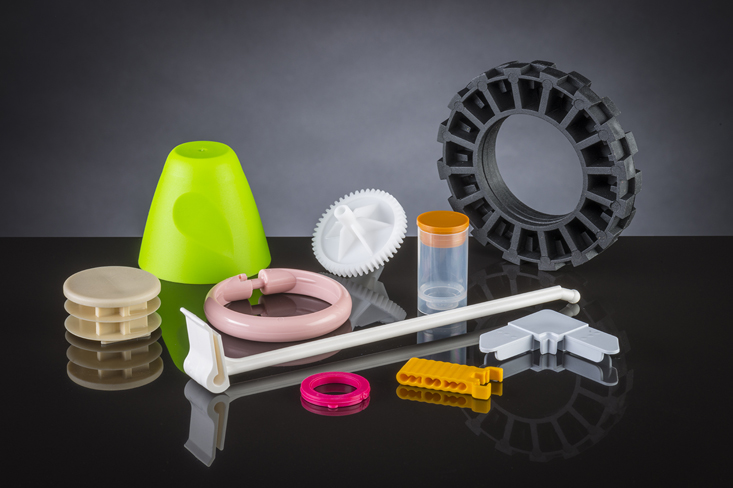
With hundreds of commodity and engineering resins available on the market today, the material selection process for plastic injection molding jobs can often seem daunting at first.
At The Rodon Group, we understand the unique benefits and properties of different types of plastics and work closely with clients to find the best fit for their project.
What Are Plastic Resins?
We live in a world surrounded by plastic resins. Due to their several desirable properties, plastic resins can be found in everything from bottles and containers to automotive and medical components and much more. Plastic resins include a large family of materials that each have their own unique properties that make them ideal for different applications. When choosing the right resin for your project, it’s important to understand what each type has to offer.
What Is the Difference Between Resin and Plastic?
Resin and plastic are both important compounds
but feature some key differences, including:
- Origin. While resins are naturally occurring in plants, plastics are synthetic and are typically derived from petrochemicals.
- Definition. Plastic is a type of synthetic resin, whereas resins are amorphous compounds that can either be semi-solid or solid.
- Stability and impurities. Plastics are more stable than resin and lack impurities. With resins, impurities cannot be avoided.
- Hardness. Plastic is dense and hard, while resin is typically a gluey and viscous substance.
- Environmental impact. Since resin is natural, it offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to plastic. Plastic degrades slowly and often has toxic additives that can lead to environmental pollution.
Common Applications for Plastic Resin Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is compatible with a wide range of resin materials. When determining the right resin for your needs, it’s important to understand the needs of your particular application. Common applications for different injection molding resins include:
ABS
Injection-molded ABS is used in a wide variety of applications, including plastic wall plates for electrical outlets, protective headgear, keyboard keys, electronic components, and automotive components such as auto body parts, wheel covers, and dashboards. It is also used for a range of industrial fittings, sports equipment, and consumer goods.
Celson® (Acetal)
Because of its low coefficient of friction, injection-molded Celson® is ideal for pulley wheels, conveyor belts, gears, and bearings. This material can also be found in various high-performance engineering components, lock systems, firearms, eyeglass frames, and fasteners.
Polypropylene
Injection-molding polypropylene is used in a wide variety of industrial, commercial, and consumer applications. For example, it can be found in power tool bodies, appliances, packaging components, sporting goods, storage containers, and children’s toys.
HIPS
Because HIPS features a higher impact strength, it can be found in appliances, printing equipment, signage, and equipment components. Other common applications include children's toys and electrical components.
LDPE
Due to its flexibility and resistance to moisture and chemicals, injection-molded LDPE is often used for applications including medical device components, wire and cable insulators, toolboxes, and children’s toys.
How Are Plastic Resins Made?
Manufacturers create plastic resins through the “cracking process,” which involves heating hydrocarbons to break down the larger molecules into propylene, ethylene, or other types of hydrocarbons. These monomers then undergo polymerization reactions to create polymer resins, which can then be collected for further processing, such as the addition of plasticizers, flame-retardant chemicals, dyes, and more.
After the cracking process, the compounds are formed into polymers, which can be combined to make the ideal plastic resin featuring the characteristics needed for the intended application. Once the desired resin is formed, it can be used in the injection molding process to create the desired products.